Hirotaka UJIOKA, Mika ARAKI, Kai MORINAGA, Masaaki IWAMOTO, Yuri IWATA, Akitoshi IWAMOTO, Miki KATSUKI, Hanano TANAKA
Proceedings of the IASS Annual Symposium 2023
Integration of Design and Fabrication
10–14 July 2023, Melbourne, Australia
Integration of Design and Fabrication
10–14 July 2023, Melbourne, Australia
Based on a biomimetics approach, a new method was developed for creating porous curved surfaces by applying the auxetic structures, inspired by the cellular morphological changes of floral organs. Free-form surface is obtained by suspending thin metal plate with equilateral triangular repeated incision under equally distributed load. By changing the incision pattern, the form can be freely changed.
Morphogenesis System of Floral Meristem in Plants
Auxetic Mechanism
Based on a biomimetic approach, it is expected that a new form-finding method, which can efficiently create complex three-dimensional shapes such as those of plant flowers can be developed by generating materials with non-uniform stiffness distribution.
As a method for fabricating panels with nonuniform stiffness distribution, this thesis proposes the application of an auxetic pattern of incisions to thin sheets.
Auxetic mechanism: The process of expansion from left to right.
A paper model experiment to understand the correlation between the auxetic pattern and the curved surface shape after suspension was conducted. Four paper models with different patterns were prepared to observe the relationship between the incision angle (θ) and the sag after suspension, and it was found that the sag decreased as the angle (θ) increased.
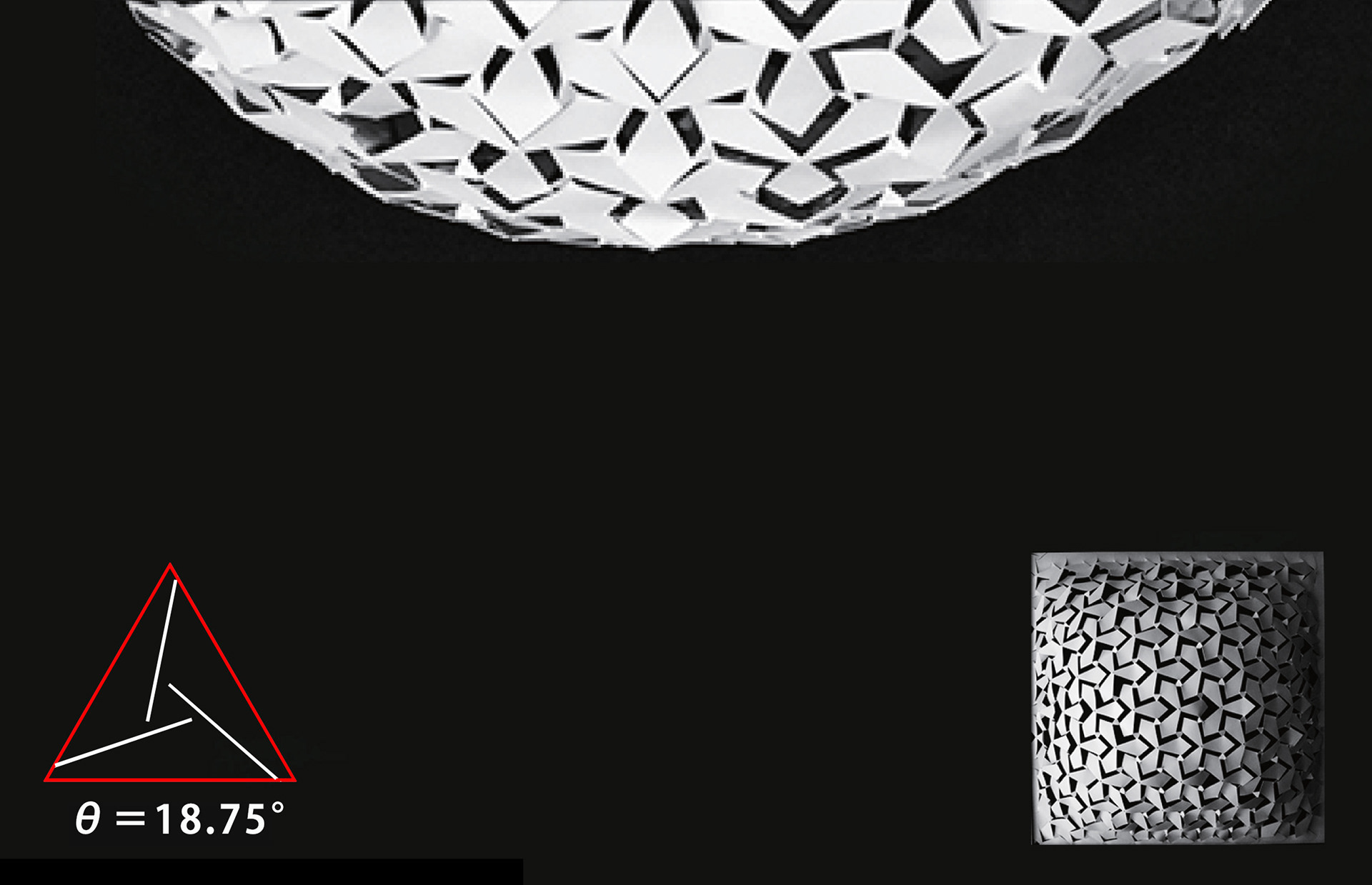

Paper model experiment
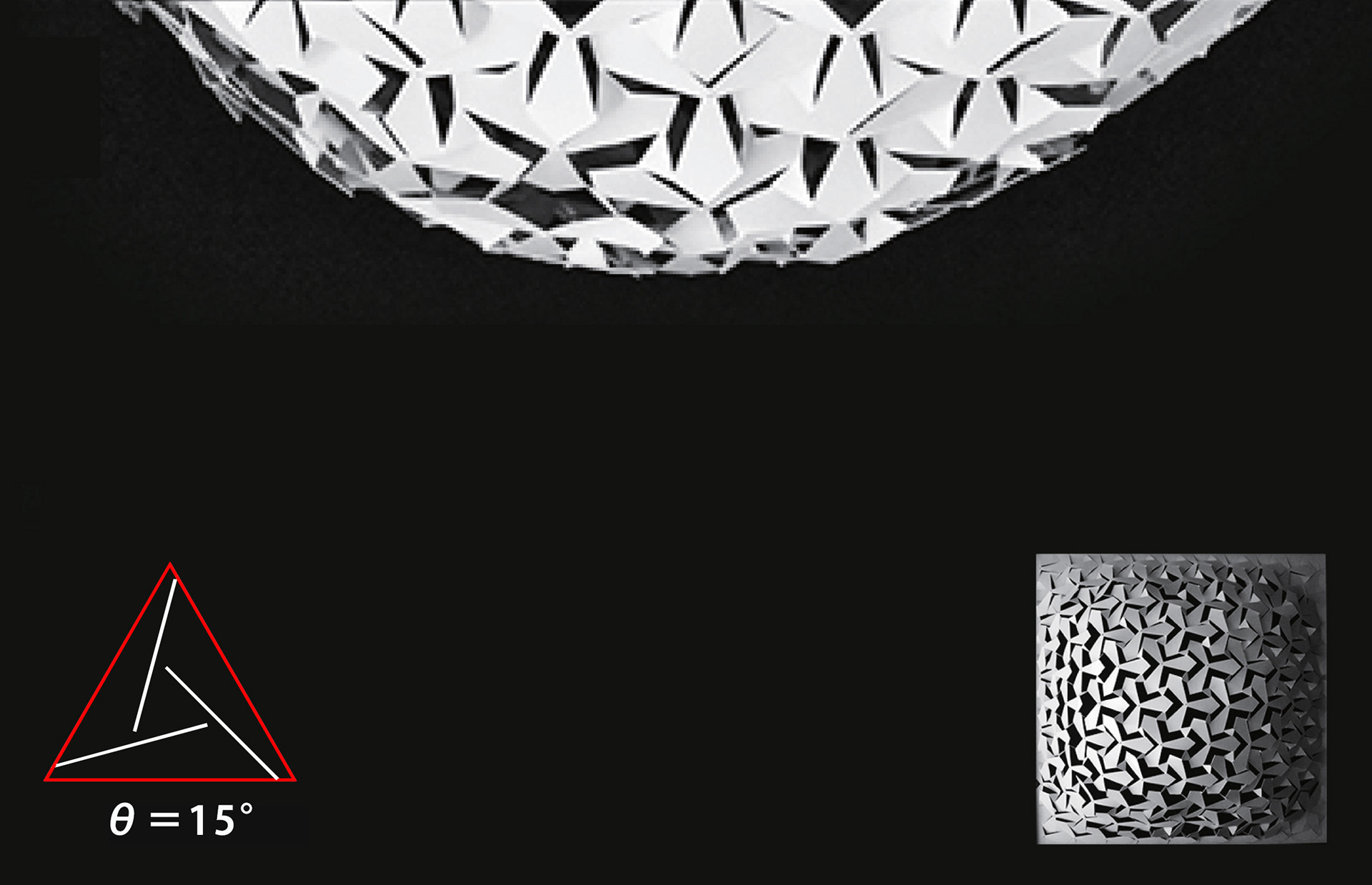

Paper model experiment
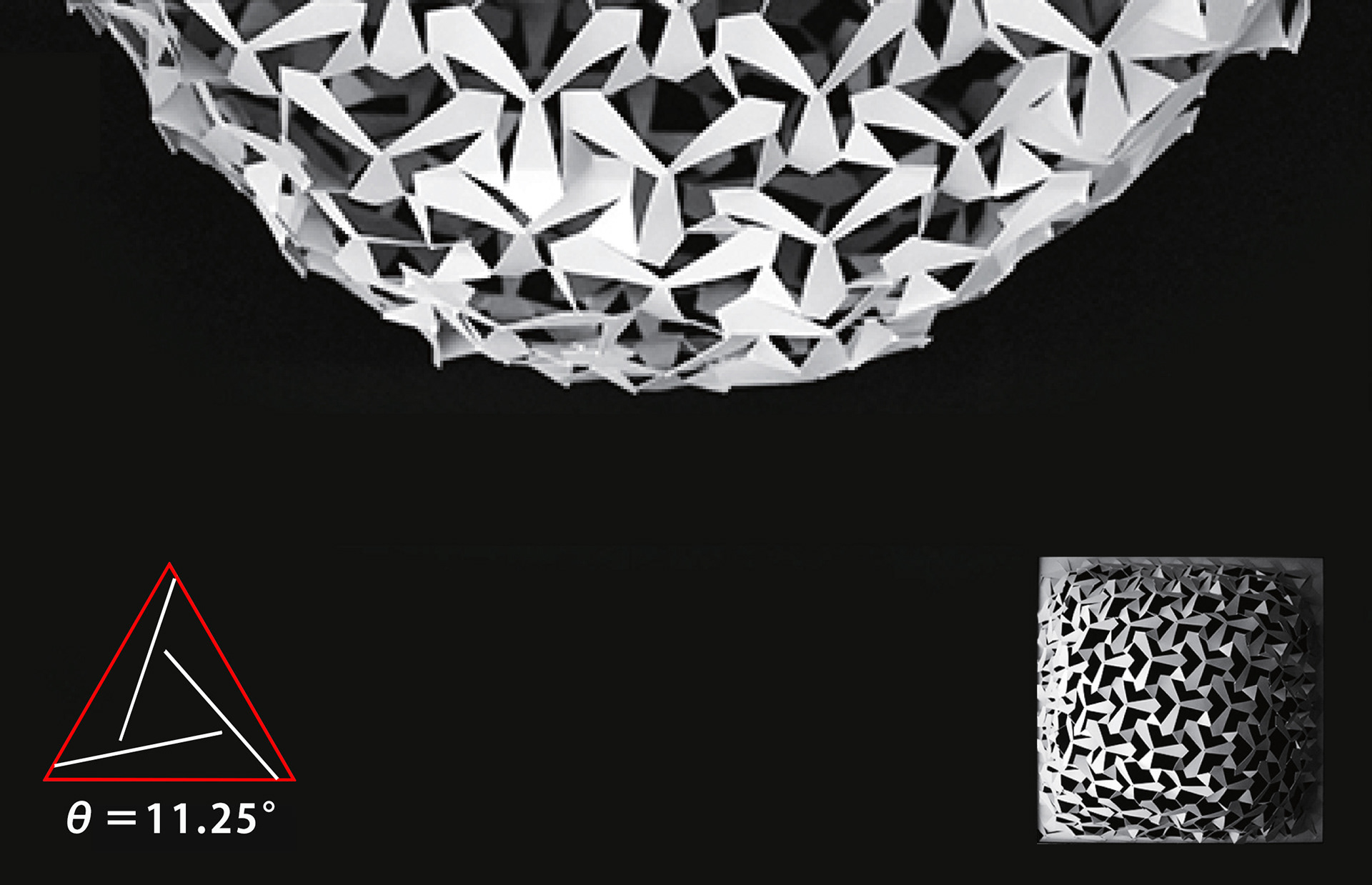

Paper model experiment
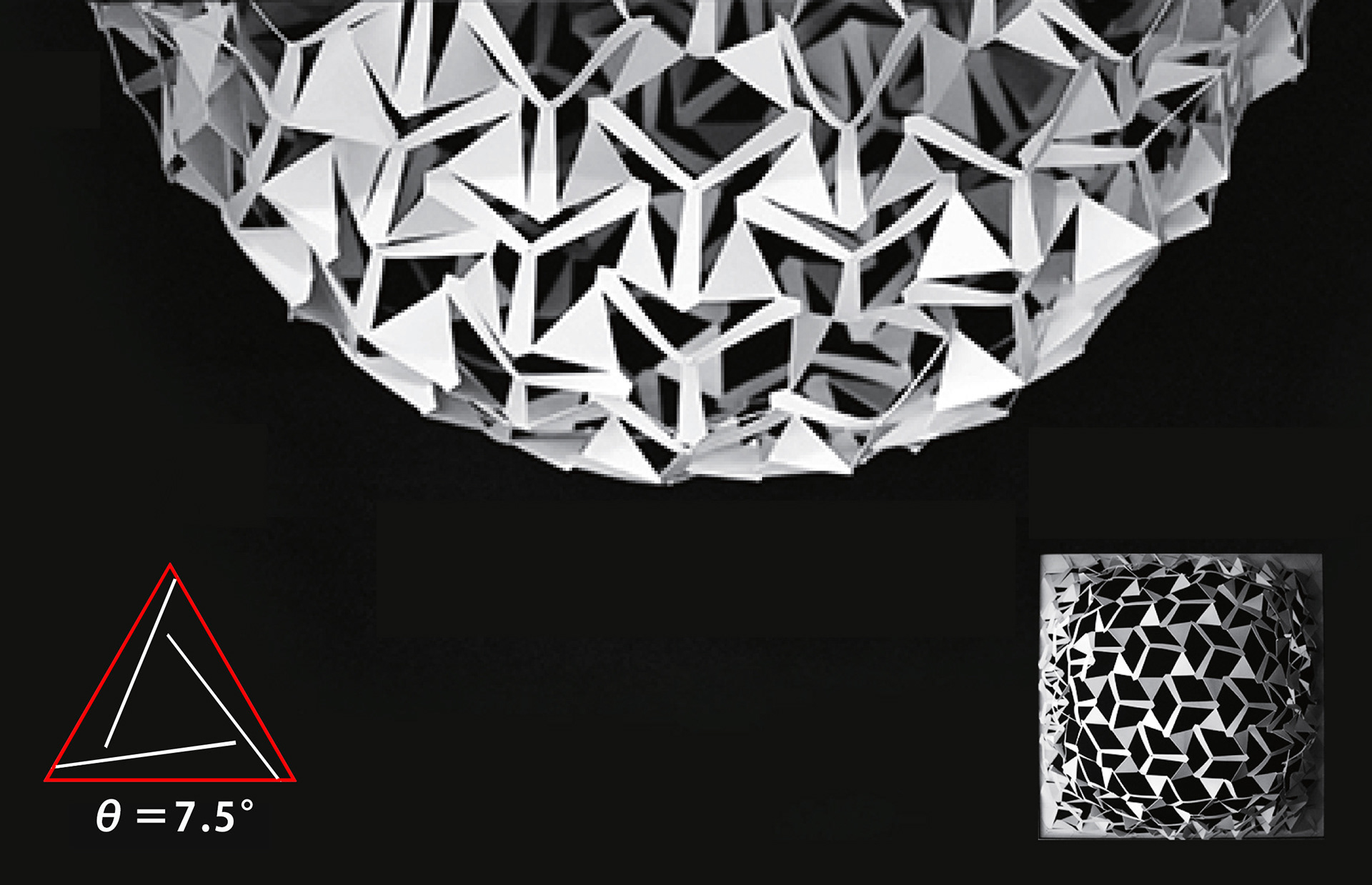

Paper model experiment
A surface material with nonuniform stiffness distribution can be created by making periodic random incisions with different angles on a thin metal plate, which is then suspended by an equally distributed load to obtain a free-form curved surface. By controlling the incision pattern, a free-form surface can be obtained after the suspension.
Image of a suspended form created by an auxetic pattern with various angles of incision (Kent paper model).
Material Tensile Tests
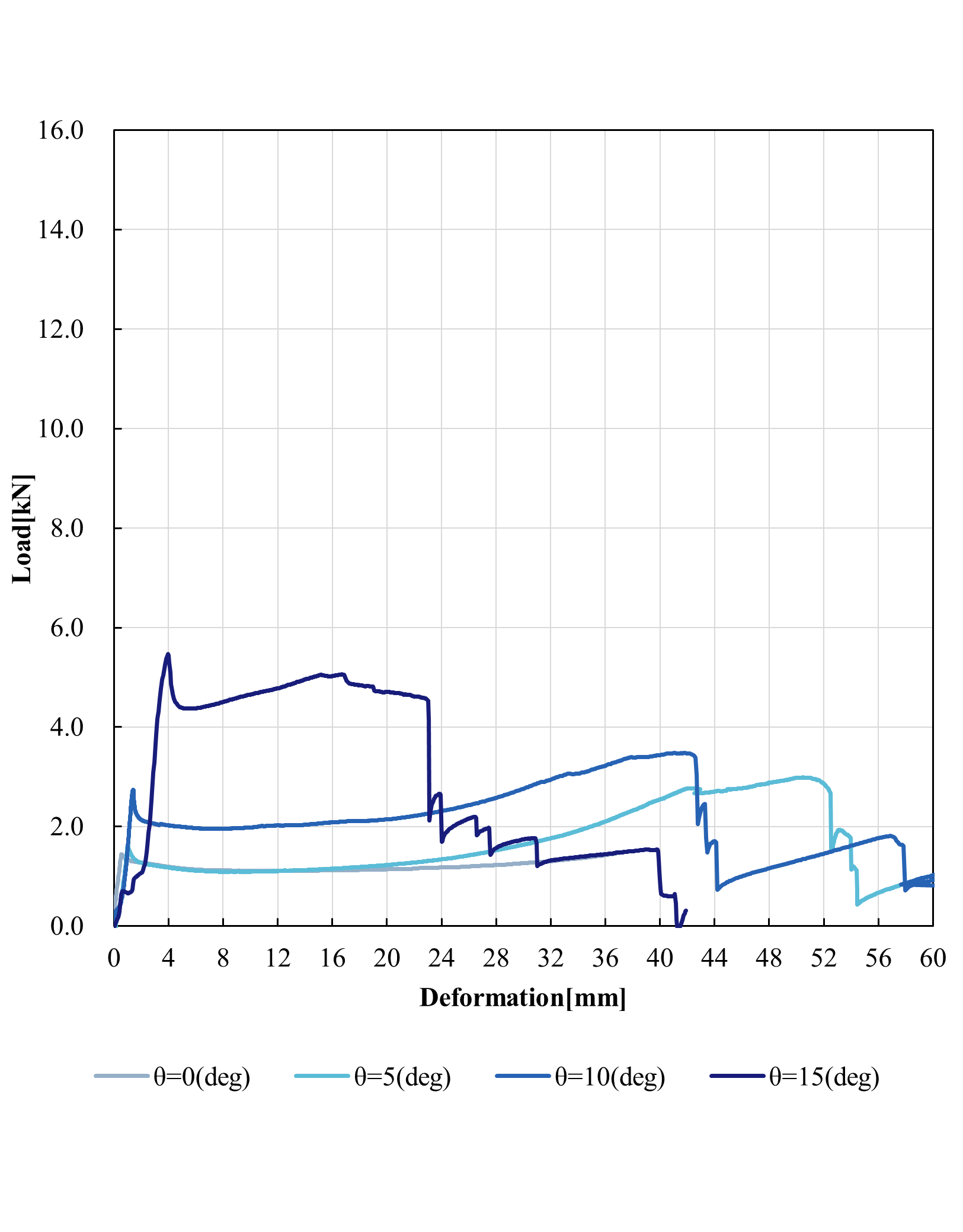
Load-deformation curves(e=5.0mm)
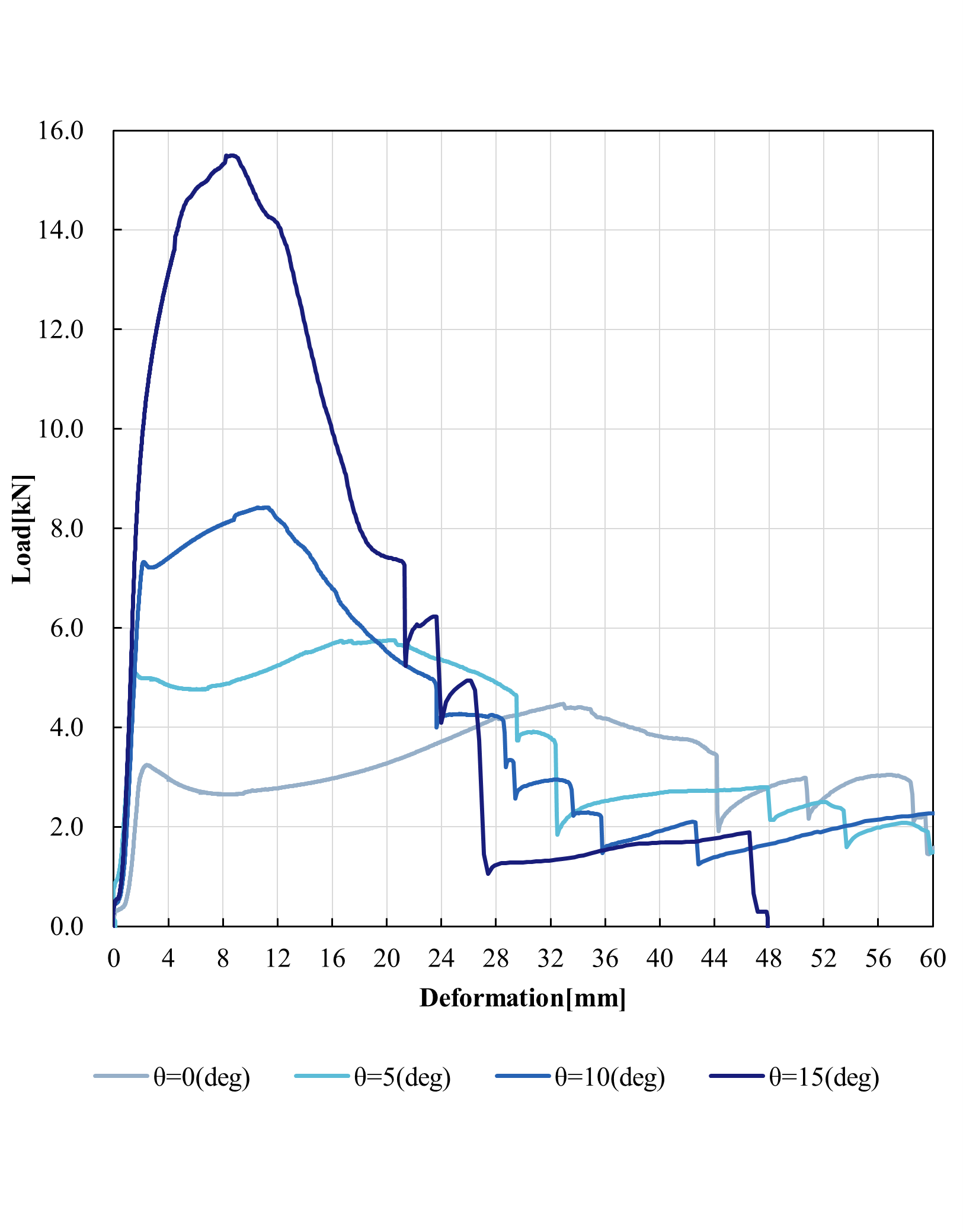
Load-deformation curves(e=10.0mm)
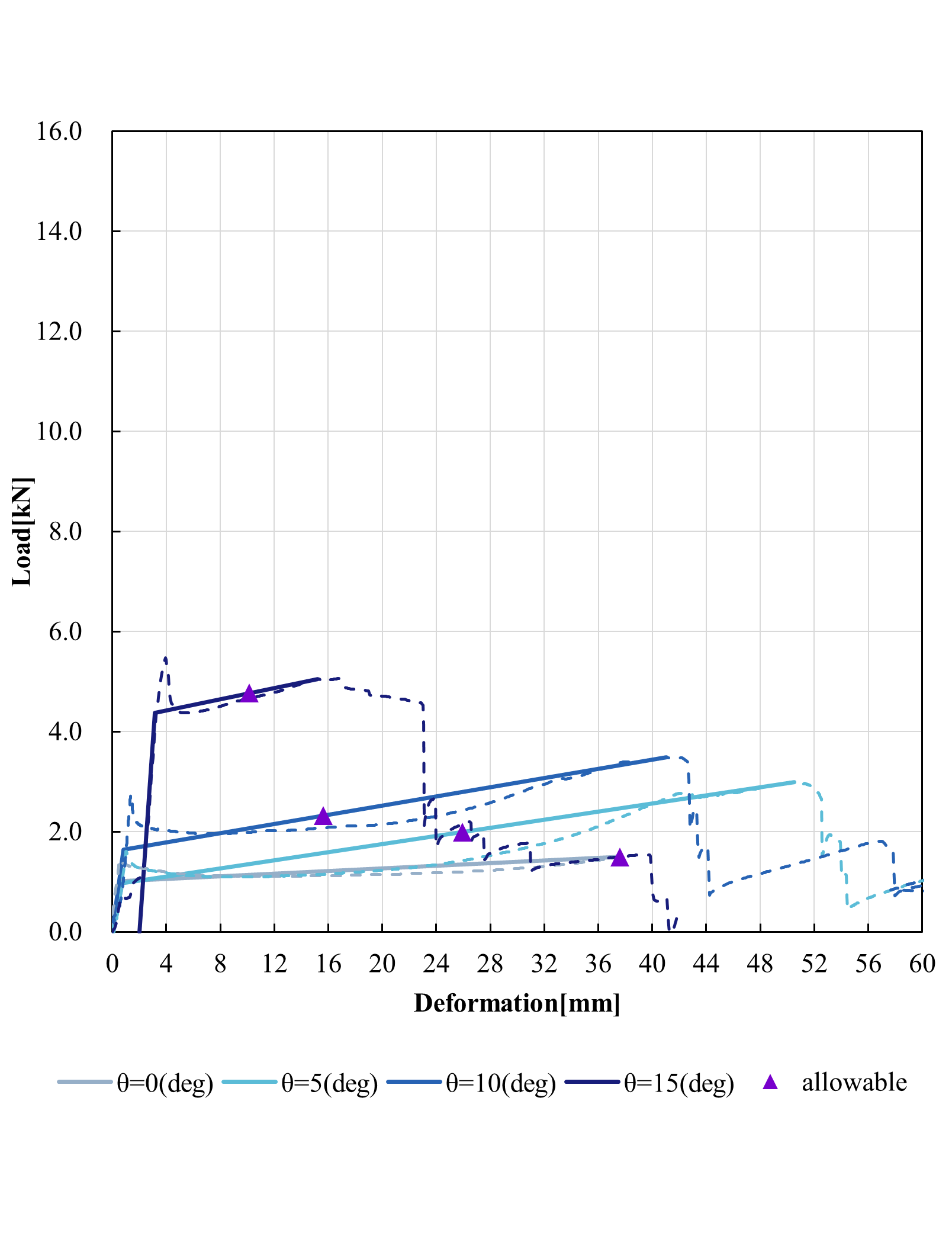
Bi-linear modeling(e=5.0mm)
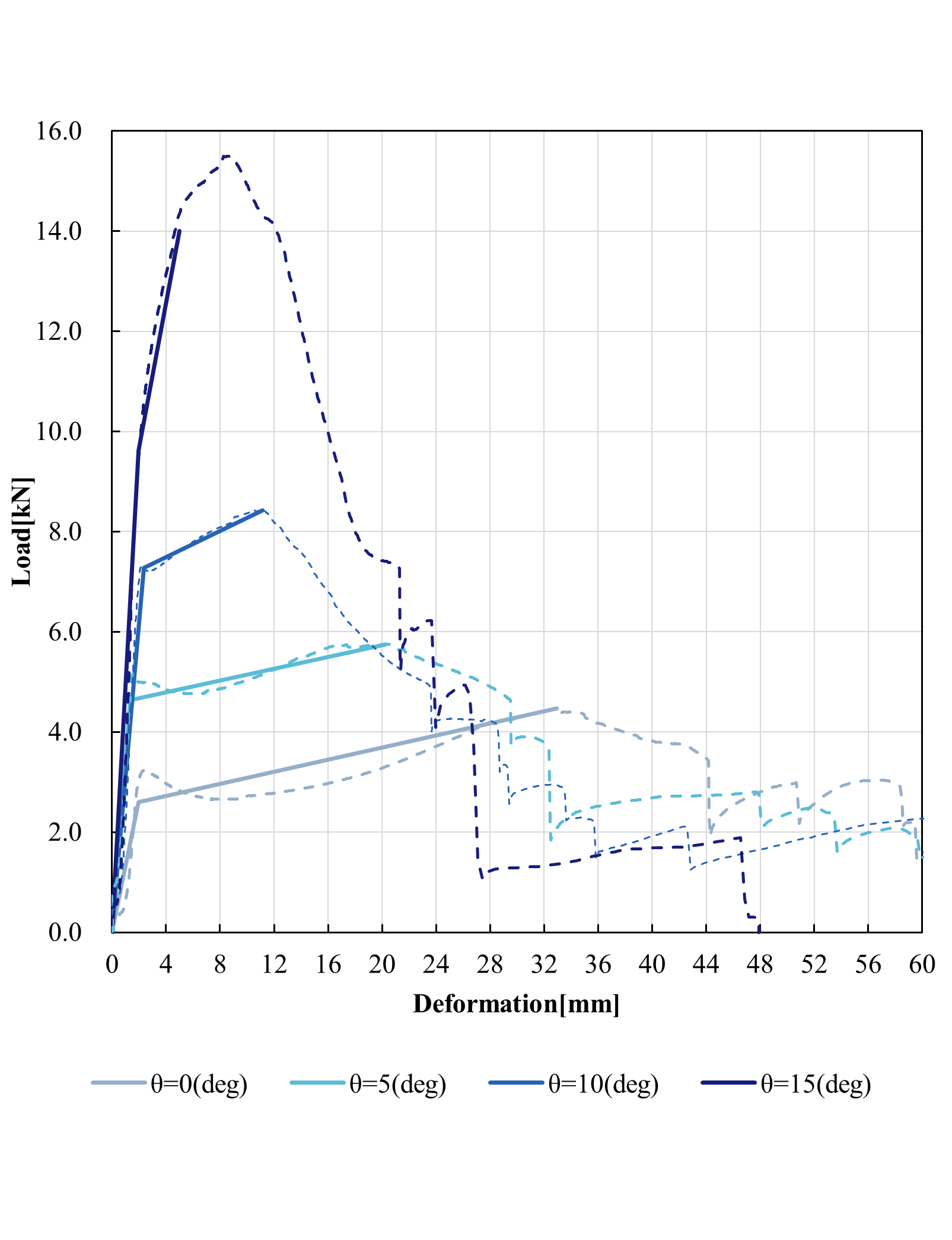
Bi-linear modeling(e=10.0mm)
Structural Analysis Method
An incremental load analysis method to find the form under distributed load. - Geometric nonlinear analysis considering material nonlinearities according to the experimental results.
The Mock-up
This work was supported by MEXT KAKENHI Grant Numbers 19H05358 (to A.I.) and 21H003759 (to A.I.). We thank Edanz (https://jp.edanz.com/ac) for editing a draft of this manuscript.